Neurogenic pulmonary oedema secondary to a seizure: A case report and review of the literature.
Edema pulmonar neurogénico secundario a una convulsión: Descripción de un caso y revisión de la literatura

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Ninguna publicación, nacional o extranjera, podrá reproducir ni traducir sus artículos ni sus resúmenes sin previa autorización escrita del editor; sin embargo los usuarios pueden descargar la información contenida en ella, pero deben darle atribución o reconocimiento de propiedad intelectual, deben usarlo tal como está, sin derivación alguna.
Show authors biography
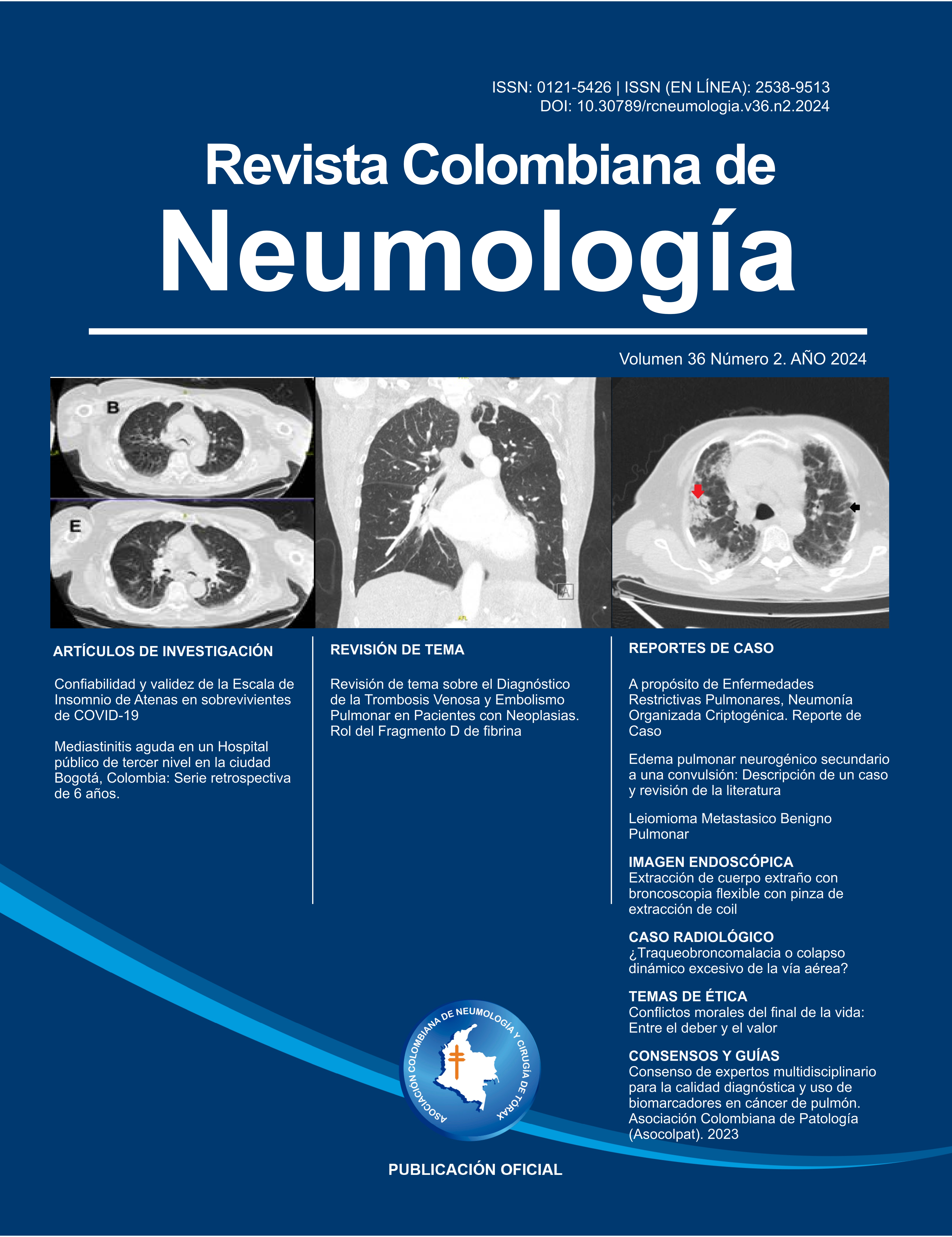
Dyspnea is a common reason for consultation in the emergency department, may be the main manifestation of pulmonary edema, which can be classified as cardiogenic or non-cardiogenic. Within the latter, neurogenic pulmonary edema has been described as a rare complication evidenced in patients with central nervous system lesions, which usually resolves within 48-72 hours after the onset of symptoms. This paper presents a case of a 53-year-old female patient admitted to the emergency department with a generalized tonic epileptic seizure and desaturation, chest imaging showing multilobar alveolar opacities. During the hospitalization, cardiogenic pulmonary edema, pulmonary infection and aspiration pneumonia were ruled out. The clinical and imaging course of the patient confirms self-limited neurogenic pulmonary edema.
Article visits 633 | PDF visits 322
Downloads
- Baumann A, Audibert G, McDonnell J, Mertes PM. Neurogenic pulmonary edema. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007;51(4):447–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01276.x
- Busl KM, Bleck TP. Neurogenic pulmonary edema. Crit Care Med. 2015;43(8):1710–5. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001101.
- Suhail Najim M, Ali Mohammed Hammamy R, Sasi S. Neurogenic pulmonary edema following a seizure: A case report and literature review. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2019:6867042. doi: 10.1155/2019/6867042.
- Davison DL, Terek M, Chawla LS. Neurogenic pulmonary edema. Crit Care. 2012;16(2):212. doi: 10.1186/cc11226.
- Finsterer J. Neurological perspectives of neurogenic pulmonary edema. Eur Neurol. 2019;81(1–2):94–102. Doi: 10.1159/000500139
- Sacher DC, Yoo EJ. Recurrent acute neurogenic pulmonary edema after uncontrolled seizures. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2018; 3483282. Doi: 10.1155/2018/3483282
- Romero Osorio OM, Abaunza Camacho JF, Sandoval Briceño D, Lasalvia P, Narino Gonzalez D. Postictal neurogenic pulmonary edema: Case report and brief literature review. Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2018;9:49–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ebcr.2017.09.003
- Romero Osorio OM, Abaunza Camacho JF, Sandoval Briceno D. Edema pulmonar postictal: revisión de la bibliografía. Rev Neurol. 2019;68(8):339–45. doi: 10.33588/rn.6808.2018356
- Kennedy JD, Hardin KA, Parikh P, Li C-S, Seyal M. Pulmonary edema following generalized tonic clonicseizures is directly associated with seizure duration. Seizure. 2015;27:19–24. Doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2015.02.023
- Fontes RB, Aguiar PH, Zanetti MV, Andrade F, Mandel M, Teixeira MJ. Acute neurogenic pulmonary edema: case reports and literature review. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2003;15(2):144–50. doi: 10.1097/00008506-200304000-00013
- Demling R, Riessen R. Pulmonary dysfunction after cerebral injury. Crit Care Med. 1990;18(7):768–74. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199007000-00019
- Mahdavi Y, Surges R, Nikoubashman O, Olaciregui Dague K, Brokmann JC, Willmes K, et al. Neurogenic pulmonary edema following seizures: A retrospective computed tomography study. Epilepsy Behav. 2019;94:112–7. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.02.006
- Zhao H, Lin G, Shi M, Gao J, Wang Y, Wang H, et al. The mechanism of neurogenic pulmonary edema in epilepsy. J Physiol Sci. 2014;64(1):65-72. doi: 10.1007/s12576-013-0291-6