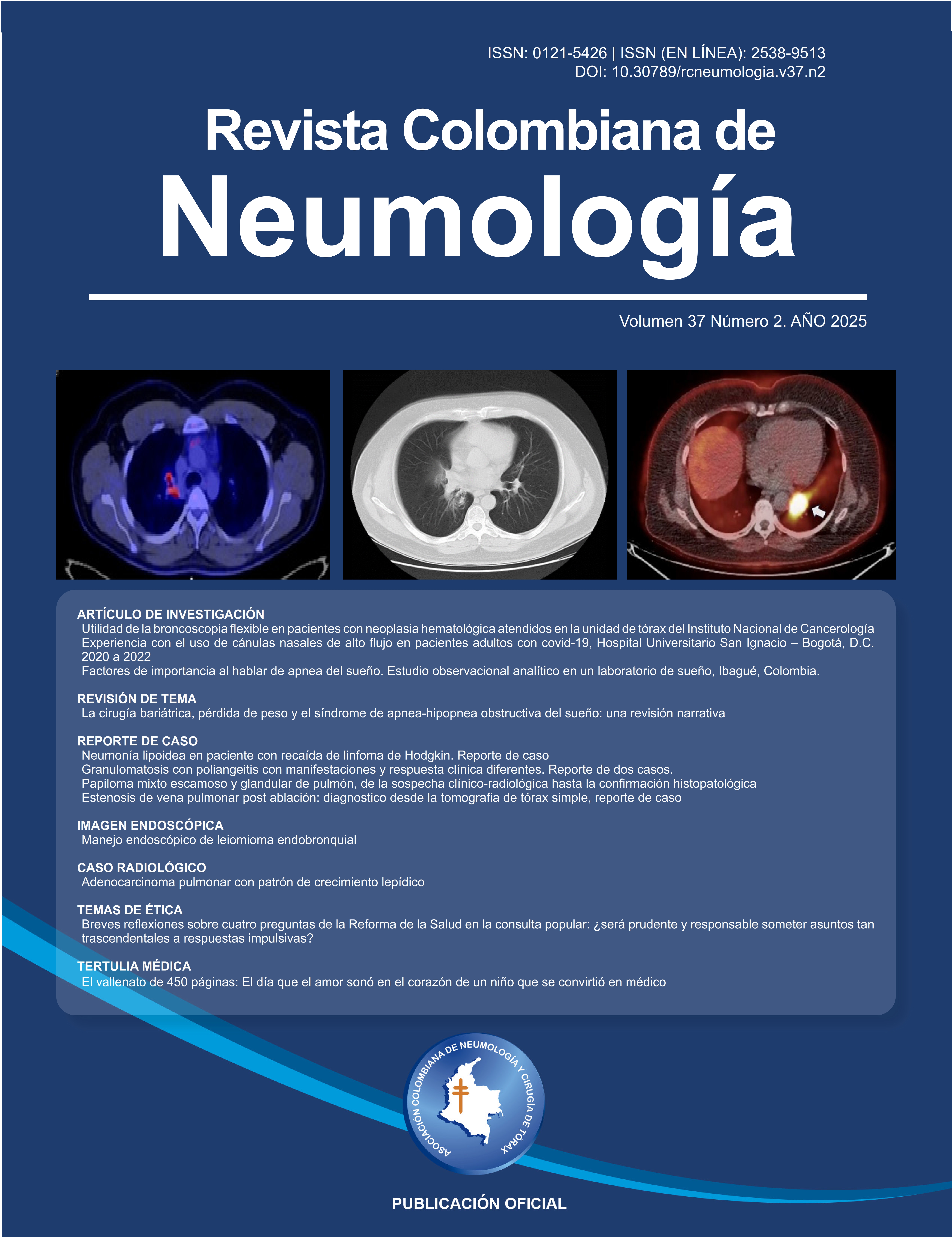
Endogenous lipoid Pneumonia in a patient with relapse from a Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Neumonía lipoidea endógena en paciente con recaída de linfoma de Hodgkin. Reporte de caso

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Ninguna publicación, nacional o extranjera, podrá reproducir ni traducir sus artículos ni sus resúmenes sin previa autorización escrita del editor; sin embargo los usuarios pueden descargar la información contenida en ella, pero deben darle atribución o reconocimiento de propiedad intelectual, deben usarlo tal como está, sin derivación alguna.
Show authors biography
We present the case of endogenous lipoid pneumonia treated in a high-complexity hospital. A 26-year-old patient with a history of relapsed Hodgkin's lymphoma who consulted for a persistent dry cough with chest images showing a parahilar pulmonary mass on the right side; metabolically active. He undergoes a lung biopsy to rule out malignancy. In the histological sections, a distorted lung architecture is observed due to the occupation of alveolar spaces by lipid material degraded by multinucleated macrophages, which are characterized by cytoplasmic microvacuoles, confirming a pattern of endogenous lipoid pneumonia. After an exhaustive search for the etiology, it was considered by a multidisciplinary board that it was due to his underlying lymphoma. Segmental pulmonary lavage by bronchoscopy, combined with systemic steroids, is a therapeutic approach used in managing specific conditions. With the above, the symptoms are resolved, and partial improvement in the pulmonary infiltrates has been achieved. The patient is currently being followed up without relapse of pulmonary pathology. The presentation of endogenous lipoid pneumonia is the least common among lipoid pneumonias; the case report and review of the topic lend their value, given that the diagnosis is frequently overlooked due to its differential diagnosis with infectious and/or oncological processes.
Article visits 105 | PDF visits 79
Downloads
- Hadda V, Khilnani GC. Lipoid pneumonia: an overview. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010 Dec;4(6):799-807. doi: https://doi.org/10.1586/ers.10.74. PMID: 21128754 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1586/ers.10.74
- Byerley JS, Hernandez ML, Leigh MW, Antoon JW. Clinical approach to endogenous lipoid pneumonia. Clin Respir J. 2016 Mar;10(2):259-63. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/crj.12203. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/crj.12203
- Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Mano CM, Hochhegger B. Exogenous lipoid pneumonia. Clinical and radiological manifestations. Respir Med. 2011 May;105(5):659-66. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2010.12.001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2010.12.001
- Antoon JW, Hernandez ML, Roehrs PA, et al. Endogenous lipoid pneumonia preceding diagnosis of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Clin Respir J. 2016 Mar;10(2):246-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/crj.12197
- Betancourt, S. L., Martínez-Jiménez, S., Rossi, S. E., et al. Lipoid pneumonia: Spectrum of clinical and radiologic manifestations. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2010;194(1):103-109. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.09.3040
- Mokhlesi B, Angulo-Zereceda D, Yaghmai V. False-positive FDG-PET scan secondary to lipoid pneumonia mimicking a solid pulmonary nodule. Ann Nucl Med. 2007 Sep;21(7):411-4. . Epub 2007 Sep 25. PMID: 17876555. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0042-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0042-y
- Tahon F, Berthezene Y, Hominal S, et al. Exogenous lipoid pneumonia with unusual CT pattern and FDG positron emission tomography scan findings. Eur Radiol. 2002;12(3):S171-3.414. Ann Nucl Med. 2007;21:411–414 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-002-1659-9
- Talwar A, Mayerhoff R, London D, et al. False-positive PET scan in a patient with lipoid pneumonia simulating lung cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2004; 29:426-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.rlu.0000129123.61966.e0
- Han, C., Liu, L., Du, S., Mei, J., Huang, L., Chen, M., Lei, Y., Qian, J., Luo, J., & Zhang, M. (s.f.). Investigation of rare chronic lipoid pneumonia associated with occupational exposure to paraffin aerosol. Lishui Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Lipoid pneumonia. Pathology Outlines. Updated January 5, 2023. Disponible en: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungnontumorlipoidpneumonia.html
- Nandavaram S, Manta D. Case Report of Lipoid Pneumonia: An Unusual Etiology of a Lung Cavity. Int J Respir Pulm Med. 2018;5:076. doi: https://doi.org/10.23937/2378-3516/14100 DOI: https://doi.org/10.23937/2378-3516/1410076
- Tancredi A, Graziano P, Scaramuzzi R, et al. Exogenous Lipoid Pneumonia due to Chronic Inhalation of Oily Product Used as a Lubricant of Tracheotomy Cannula. Eurasian J Med. 2018 Jun;50(2):125-127. doi: https://doi.org/10.5152/eurasianjmed.2018.17325 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5152/eurasianjmed.2018.17325
- Betancourt SL, Martinez-Jimenez S, Rossi SE, et al. Lipoid pneumonia: Spectrum of clinical and radiologic manifestations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010 Jan;194(1):103-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.09.3040. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.09.3040
- Antoon JW, Hernandez ML, Roehrs PA, Noah TL, et al. Endogenous lipoid pneumonia preceding diagnosis of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Clin Respir J. 2016 Mar;10(2):246-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/crj.12197. Epub 2014 Sep 16. PMID: 25103284 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/crj.12197
- McDonald JW, Roggli VL, Bradford WD. Coexisting endogenous and exogenous lipoid pneumonia and pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in a patient with neurodevelopmental disease. Pediatr Pathol. 1994 May-Jun;14(3):505-11. doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/15513819409024280. PMID: 8066006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/15513819409024280
- Mark EJ, Flieder DB, Matsubara O. Treated Wegener's granulomatosis: distinctive pathological findings in the lungs of 20 patients and what they tell us about the natural history of the disease. Hum Pathol. 1997 Apr;28(4):450-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0046-8177(97)90034-4. PMID: 9104945 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0046-8177(97)90034-4
- Van der Hoven B, Stiegelis WF, van der Linden AN, et al. Lipoid pneumonitis complicating treatment of Hodgkin's disease. Neth J Med. 1993 Oct;43(3-4):183-6. PMID: 8302398.
- Leber A, Carette S, Chapman KR, et al. A 21-year-old man with systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, cough and progressive dyspnea. Can Respir J. 2010 May-Jun;17(3):e42-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/810860. PMID: 20617213; PMCID: PMC2900144. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/810860
- Nicholson AG, Wells AU, Hooper J, et al. Successful treatment of endogenous lipoid pneumonia due to Niemann-Pick Type B disease with whole-lung lavage. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002 Jan 1;165(1):128-31. doi: https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.165.1.2103113. PMID: 11779742. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.165.1.2103113
- Berghaus TM, Haeckel T, Wagner T, von Scheidt W, Schwaiblmair MG. Endogenous lipoid pneumonia associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Lancet. 2007 Mar 31;369(9567):1140. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60530-3. PMID: 17398313. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60530-3
- Barta Z, Szabo GG, Bruckner G, et al. Endogenous lipoid pneumonia associated with undifferentiated connective tissue disease (UCTD). Med Sci Monit. 2001 Jan-Feb;7(1):134-6. PMID: 11208509
- Shang L, Gu X, Du S, Wang Y, et al for CAP-China Network. The efficacy and safety of therapeutic lung lavage for exogenous lipoid pneumonia: A systematic review. Clin Respir J. 2021 Feb;15(2):134-146. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/crj.13273 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/crj.13273
- Ahmed A, Gupta V, Fleming DA, Aggarwal K. Pulmonary tuberculosis causing lipoid pneumonia. Mo Med. 2007 Sep-Oct;104(5):446-7. PMID: 18018534.
- Au WY, Lie AK, Cheng VC, Cheng LC, et al. Successful lung transplantation for post-BMT bronchiolitis obliterans and lipoid pneumonia associated with atypical mycobacterium and aspergillosis infection. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2007 Aug;26(8):870-2. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2007.05.015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2007.05.015