Endoscopic management of endobronchial leiomyoma
Manejo endoscópico del leiomioma endobronquial

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Ninguna publicación, nacional o extranjera, podrá reproducir ni traducir sus artículos ni sus resúmenes sin previa autorización escrita del editor; sin embargo los usuarios pueden descargar la información contenida en ella, pero deben darle atribución o reconocimiento de propiedad intelectual, deben usarlo tal como está, sin derivación alguna.
Show authors biography
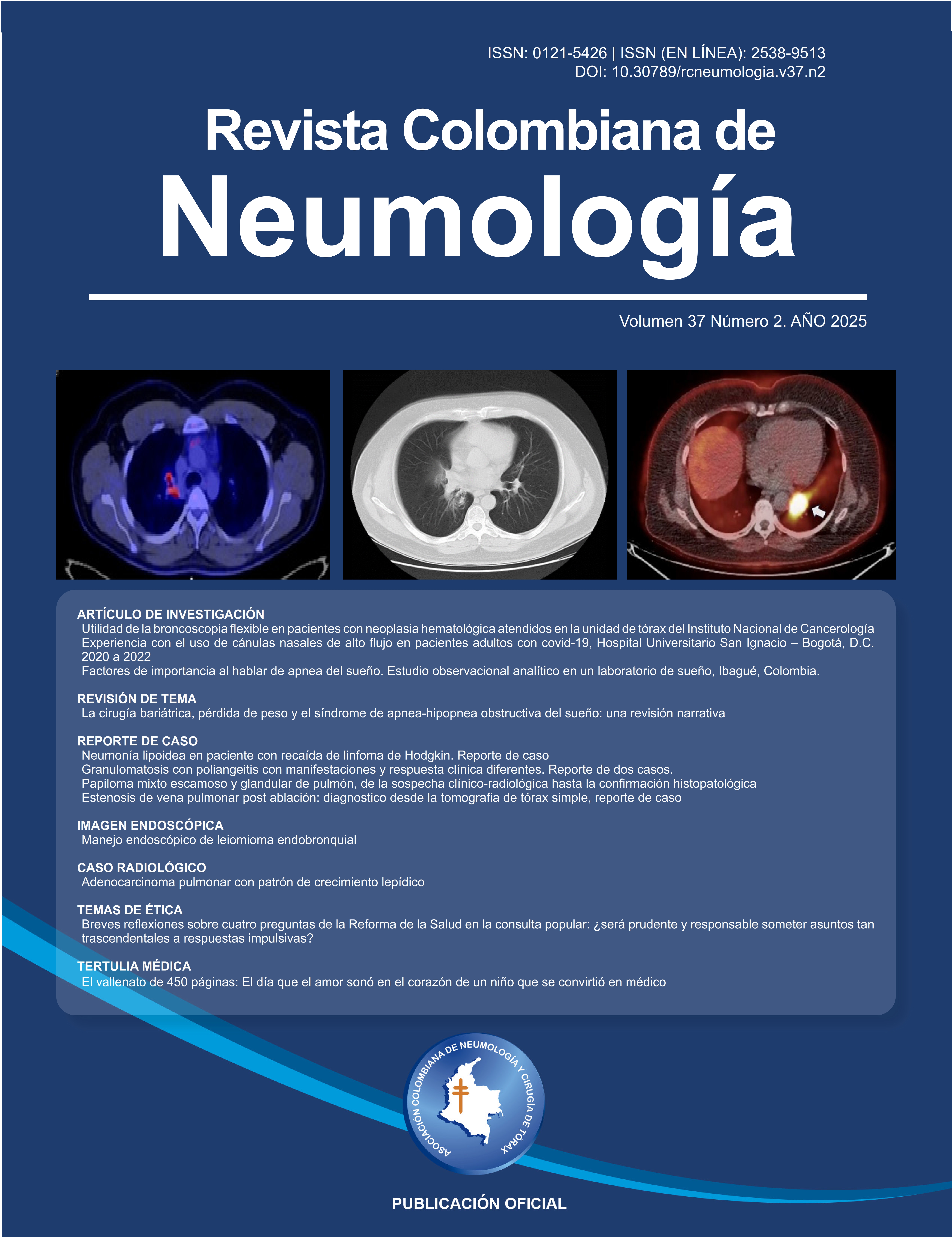
Endobronchial leiomyoma is a rare tumor of mesodermal origin that can mimic other obstructive pathologies and requires diagnosis through bronchoscopy and histological analysis. Endoscopic management using minimally invasive techniques has proven to be safe and effective, avoiding the need for extensive pulmonary resections. We present the case of a 26-year-old female patient with unilateral dyspnea and wheezing. A chest computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a space-occupying lesion in the right main bronchus. Bronchoscopy showed a 90% obstruction of the bronchial lumen. The tumor was mechanically resected using forceps, and the procedure was complemented with argon plasma coagulation, resulting in complete restoration of the airway. Histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of endobronchial leiomyoma. A follow-up fiberoptic bronchoscopy performed six months later showed no evidence of recurrence.
Article visits 64 | PDF visits 44
Downloads
- Arrigoni MG, Woolner LB, Bernatz PE, Miller WE, Fontana RS. Benign tumors of the lung. A ten-year surgical experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1970 Oct;60(4):589-99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5223(19)42341-6
- White SH, Ibrahim NB, Forrester-Wood CP, Jeyasingham K. Leiomyomas of the lower respiratory tract. Thorax. 1985 Apr 1;40(4):306-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.40.4.306
- Llobregat Poyan N, Mentrida Rodríguez JM, González Aragoneses F, Orusco Palomino E, Pérez Gallardo M, Folque Gómez E, et al. Leiomiona de pulmón: a propósito de un caso. Arch Bronconeumol. 1988 Sep;24(5):215-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-2896(15)31816-0
- Martín Díaz E, Aman Obrer A, Hostalet Robles E, Ramón Capilla M, Cantó Armengod A. Leiomioma endobronquial a propósito de un caso. Neumosur Rev Asoc Neumólogos Su. 1997;9(4):59-63.
- Yamada H, Katoh O, Yamaguchi T, Natsuaki M, Itoh T. Intrabronchial Leiomyoma Treated by Localized Resection Via Bronchotomy and Bronchoplasty. Chest. 1987 Feb;91(2):283-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.91.2.283
- Tan JHY, Takano AM, Hsu AAL. Resection with preserved histologic morphology of a rare tumour via bronchoscopic cryosurgery. J Thorac Dis. 2016 Oct;8(10):2964-7. doi: ttps://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2016.10.08 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2016.10.08